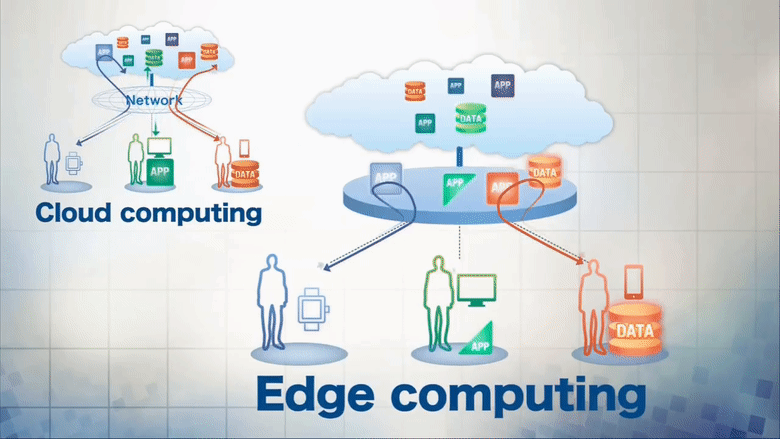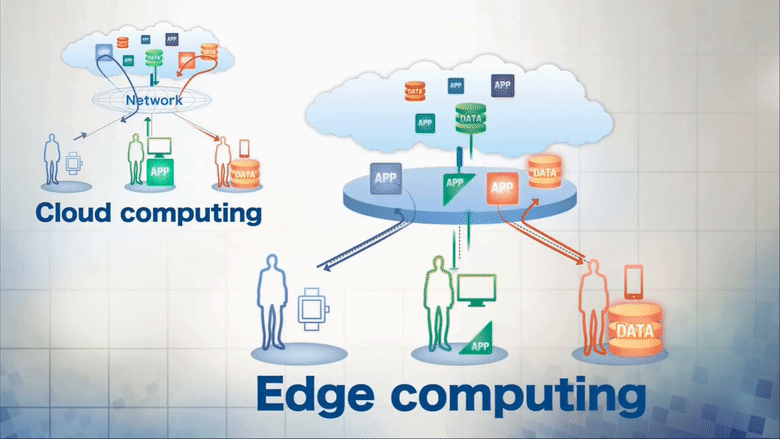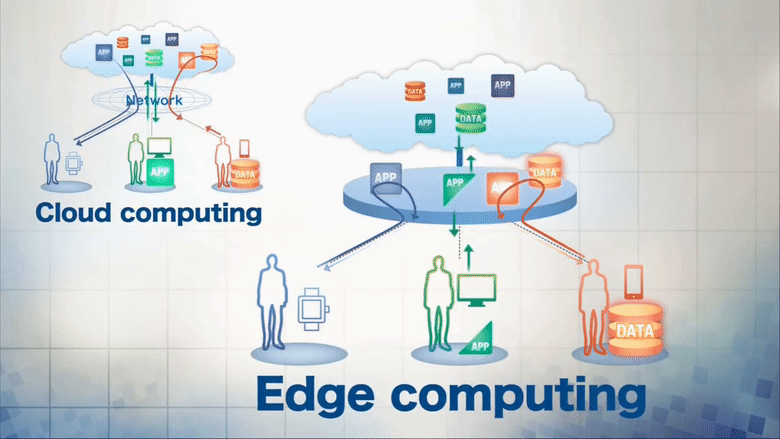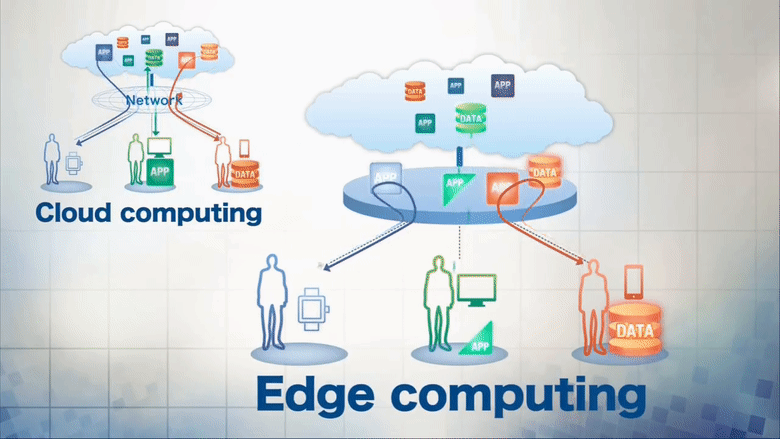
Edge computing is a distributed information technology (IT) architecture in which client data is processed at the periphery of the network, as close to the originating source as possible.
Data is the lifeblood of modern business, providing valuable business insight and supporting real-time control over critical business processes and operations. Today’s businesses are awash in an ocean of data, and huge amounts of data can be routinely collected from sensors and IoT devices operating in real time from
Because of the increase in connected devices it will change the way we live, work and interact with technology. In the next 5 years there will be a rise in smart devices to around 75 billion globally, this we can name as a new era of hyper-connectivity. These IOT devices are connected to the cloud to process data using the internet as a communication medium. This leads to high communication cost and also causes problems for some hard real time delay sensitive applications such as automated vehicles, video surveillance, manufacturing systems etc. It was seen that in technologies like IOT the delay involved in processing data using cloud resources will be high. It is necessary to perform computing, communication / networking and control locally leading to the idea of edge computing.
Why is edge computing important?
Computing tasks demand suitable architectures, and the architecture that suits one type of computing task doesn’t necessarily fit all types of computing tasks. Edge computing has emerged as a viable and important architecture that supports distributed computing to deploy compute and storage resources closer to — ideally in the same physical location as — the data source. In general, distributed computing models are hardly new, and the concepts of remote offices, branch offices, data center colocation and cloud computing have a long and proven track record.
But decentralization can be challenging, demanding high levels of monitoring and control that are easily overlooked when moving away from a traditional centralized computing model. Edge computing has become relevant because it offers an effective solution to emerging network problems associated with moving enormous volumes of data that today’s organizations produce and consume. It’s not just a problem of amount. It’s also a matter of time; applications depend on processing and responses that are increasingly time-sensitive.
![Network World - How Edge Computing Works [diagram]](https://images.idgesg.net/images/article/2017/09/nw_how_edge_computing_works_diagram_1400x1717-100736111-large.jpg?auto=webp&quality=85,70)
Some Important Factor for which we are using Edge Computing:-
- Latency :–
Because of low latency some applications may fail
E.g.: – Health care, Financial transactions etc.
Some applications generate big amount of data which it require more bandwidth to send to cloud
E.g.:- smart surveillance systems
Edge computing use cases
There are as many different edge use cases as there are users – everyone’s arrangement will be different – but several industries have been particularly at the forefront of edge computing. Manufacturers and heavy industry use edge hardware as an enabler for delay-intolerant applications, keeping the processing power for things like automated coordination of heavy machinery on a factory floor close to where it’s needed. The edge also provides a way for those companies to integrate IoT applications like predictive maintenance close to the machines. Similarly, agricultural users can use edge computing as a collection layer for data from a wide range of connected devices, including soil and temperature sensors, combines and tractors, and more. (Read more about IoT on the farm: Drones and sensors for better yields)
The hardware required for different types of deployment will differ substantially. Industrial users, for example, will put a premium on reliability and low-latency, requiring ruggedized edge nodes that can operate in the harsh environment of a factory floor, and dedicated communication links (private 5G, dedicated Wi-Fi networks or even wired connections) to achieve their goals. Connected agriculture users, by contrast, will still require a rugged edge device to cope with outdoor deployment, but the connectivity piece could look quite different – low-latency might still be a requirement for coordinating the movement of heavy equipment, but environmental sensors are likely to have both higher range and lower data requirements – an LP-WAN connection, Sigfox or the like could be the best choice there.
Other use cases present different challenges entirely. Retailers can use edge nodes as an in-store clearinghouse for a host of different functionality, tying point-of-sale data together with targeted promotions, tracking foot traffic, and more for a unified store management application. The connectivity piece here could be simple – in-house Wi-Fi for every device – or more complex, with Bluetooth or other low-power connectivity servicing traffic tracking and promotional services, and Wi-Fi reserved for point-of-sale and self-checkout.
Some advantages of Edge Computing are:–
- Real time data processing.
- Real time control (M2M).
- Local data filtering and caching.
- At source data visualization.
Characteristics of Edge computing include:-Geographically distributed.
- Scalable.
- Autonomous and distributed.
- Low latency.
- Real time interactions.
Privacy and security
From a security standpoint, data at the edge can be troublesome, especially when it’s being handled by different devices that might not be as secure as centralized or cloud-based systems. As the number of IoT devices grows, it’s imperative that IT understands the potential security issues and makes sure those systems can be secured. This includes encrypting data and employing access-control methods and possibly VPN tunneling.
Furthermore, differing device requirements for processing power, electricity and network connectivity can have an impact on the reliability of an edge device. This makes redundancy and failover management crucial for devices that process data at the edge to ensure that the data is delivered and processed correctly when a single node goes down.
Overall Benefits:-
- Fast response time. (Fastest response time for triggering.
- Secure (Locally stored)
- Cost effective (No need to transport everything to the cloud).
- Reliable operations (can work without connectivity).
IoT devices are gaining momentum from wearables to vehicles to robots. As we are moving to a world with lots and lots of data, and data processing the need of a faster connection is becoming crucial. While a centralized data center or cloud for data management, processing and storage International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology. Edge computing can provide an alternative solution for this. But since the technology is still in its immaturity, it is difficult to predict its success in future. Even though, there will be more opportunities for companies to test and set up this technology. In that there are already, some use cases may prove the value of edge computing more clearly, its potential impact on our ecosystem as a whole.
#Embedded Courses in Bangalore #Embedded Courses in Hyderabad #Embedded Jobs for Freshers #Embedded C #Embedded Systems #Embedded Training in Hyderabad #Embedded Classes in Hyderabad #Embedded Systems Course in Hyderabad #Embedded Programming Courses in Hyderabad #Embedded Training in Bangalore #Embedded Classes in Bangalore #Embedded Systems Course in Bangalore #Embedded Programming Courses in Bangalore #Best Embedded Training Institute in Bangalore #Best Embedded Training Institute in Hyderabad #Embedded Training Institute in Bangalore #Embedded Training Institute in Hyderabad #Best Embedded Course in Bangalore #Best Embedded Course in Hyderabad #best iot training institute in Bangalore #best iot training institute in Hyderabad #iot training institute in bangalore #iot training institute in Hyderabad #best iot course in Bangalore #best iot course in hyderabad #Embedded Jobs in Bangalore #Embedded Jobs in Hyderabad #Iot jobs in Bangalore #IoT jobs in Hyderabad #Python Jobs in Bangalore #Python Jobs in Hyderabad #AIML #Artificial Intelligence #machine learning #Data Science Courses in Bangalore #Data Science Courses in Hyderabad #Data Science Courses #Best Data Science Training Institute #Best Data science Course #Best Python Course #Best Iot Course #Best Iot Training Institute in Bangalore #Best Iot Training Institute in Hyderabad #Iot Certification Course Bangalore #Iot Certification Course Hyderabad #Best Artificial Intelligence Training Institute Bangalore #Best Artificial Intelligence Training Institute Hyderabad #Best fullstack Training Institute in Bangalore #Best full stack Training Institute in Hyderabad #full stack Training Institute in Bangalore #full stack Training Institute in Hyderabad #Best full stack Course in Bangalore #Best full stack Course in Hyderabad
Author: Prithvi. [MBA in Digital marketing and Ecommerce]